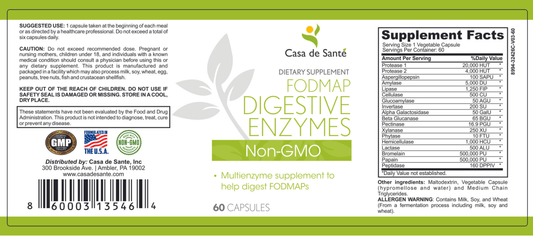
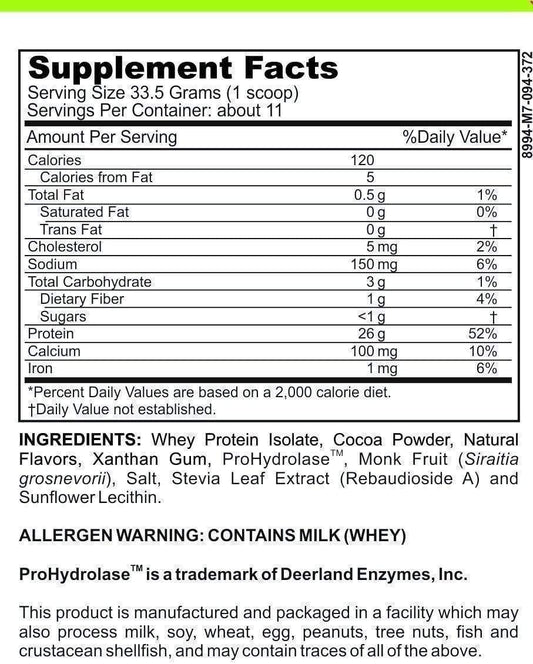
What Is Maltodextrin and Is It Dangerous?
Maltodextrin is a widely used food additive and sweetener that has gained popularity in recent years, but there has been much controversy regarding its safety and health effects. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at maltodextrin and explore the various forms, benefits, controversies, and concerns surrounding its use in food products and sports nutrition supplements.
The Composition of Maltodextrin and How It Is Made
Maltodextrin is a carbohydrate derived from starch, usually corn, rice, or potato starch. It is produced through the hydrolysis of starch, a process that breaks down the long chains of glucose molecules into shorter chains. These shorter chains are then further broken down into maltodextrin molecules. The degree of hydrolysis determines the composition of maltodextrin, which can range from dextrin to complex carbohydrates.
Maltodextrin is commonly used as a food additive due to its ability to improve texture, increase shelf life, and enhance flavor. It is often found in processed foods such as baked goods, snacks, and beverages. However, maltodextrin is also used in the pharmaceutical industry as a filler in capsules and tablets.
While maltodextrin is generally considered safe for consumption, it is important to note that it has a high glycemic index and can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This can be a concern for individuals with diabetes or those trying to manage their blood sugar levels. As with any food additive, it is important to consume maltodextrin in moderation and to be aware of its potential effects on your health.
The Different Forms of Maltodextrin: Powdered vs. Liquid
Maltodextrin comes in two forms, powdered and liquid. Powdered maltodextrin is a fine, white powder that is commonly used as a thickener, filler, and sweetener in many food products, while liquid maltodextrin is used as a carrier for flavors, colors, and other additives. Both forms have similar compositions and nutritional values, although the liquid form is slightly easier to digest.
One advantage of using powdered maltodextrin is that it has a longer shelf life than liquid maltodextrin. This makes it a popular choice for food manufacturers who need to store their ingredients for long periods of time. Additionally, powdered maltodextrin is easier to measure and mix into recipes, making it a convenient option for home cooks and bakers.
On the other hand, liquid maltodextrin is often preferred in the beverage industry because it dissolves easily in water and other liquids. This makes it a popular choice for sports drinks, energy drinks, and other beverages that require quick and easy mixing. Liquid maltodextrin is also used in the pharmaceutical industry as a binding agent for tablets and capsules.
Maltodextrin as a Food Additive: Its Uses and Benefits
Maltodextrin is commonly used as a food additive due to its versatility and many benefits. It is often used as a binder, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener, and flavor carrier in various processed foods, including baked goods, snacks, beverages, and sauces. Maltodextrin also has a mild sweetness that makes it a popular sugar substitute in various low-calorie and sugar-free products. Additionally, maltodextrin provides a source of easily digestible carbohydrates that can help boost energy levels and aid in post-workout recovery.
Another benefit of maltodextrin is its ability to improve the texture and mouthfeel of certain foods. It can create a smooth and creamy texture in products like ice cream and yogurt, and can also prevent crystallization in frozen desserts. Maltodextrin can also help improve the shelf life of certain foods by preventing moisture absorption and reducing the growth of bacteria and mold.
However, it is important to note that maltodextrin is a highly processed ingredient and may not be suitable for everyone. It has a high glycemic index, which means it can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. This can be problematic for individuals with diabetes or those who are trying to manage their blood sugar levels. Additionally, some people may experience digestive issues or allergic reactions to maltodextrin.
The Controversies Surrounding Maltodextrin's Safety
Despite its widespread use, maltodextrin has raised safety concerns due to its potential health effects. Some studies have linked maltodextrin to inflammation, gut dysbiosis, poor gut health, and increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. However, these studies are mostly observational, and more research is needed to establish a direct link between maltodextrin consumption and adverse health outcomes. It is also worth noting that maltodextrin is generally recognized as safe by the FDA and other international food safety organizations.
One of the main concerns with maltodextrin is that it is often derived from genetically modified corn. This has raised questions about the potential long-term effects of consuming genetically modified organisms (GMOs) on human health. While some studies have suggested that GMOs may have negative health effects, others have found no significant differences between GMO and non-GMO foods.
Another controversy surrounding maltodextrin is its impact on blood sugar levels. Maltodextrin has a high glycemic index, meaning it can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. This can be particularly concerning for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. However, some research has suggested that consuming maltodextrin in moderation may not have a significant impact on blood sugar levels in healthy individuals.
The Link Between Maltodextrin and Blood Sugar Levels
Maltodextrin has a high glycemic index, which means that it can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for athletes and people who need a quick source of energy, but it can also be problematic for people with diabetes or insulin resistance. Additionally, frequent consumption of high-glycemic foods like maltodextrin can lead to insulin resistance and other metabolic disorders over time.
It is important to note that not all maltodextrin is created equal. Some forms of maltodextrin are derived from corn, while others are derived from wheat. This can be a concern for people with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease, as wheat-derived maltodextrin may contain gluten. It is important to read labels carefully and choose products that are labeled as gluten-free if necessary.
While maltodextrin is often used as a food additive, it can also be found in some medications and supplements. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking to ensure that they do not contain maltodextrin or other ingredients that may affect your blood sugar levels.
Understanding the Glycemic Index of Maltodextrin
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly and how much a food raises blood sugar levels. Maltodextrin has a GI of around 85, which is higher than table sugar and many other carbohydrates. This implies that maltodextrin can cause a significant spike in blood sugar levels, and its consumption should be monitored, especially among individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
However, it is important to note that the GI of maltodextrin can vary depending on the source and processing method. Maltodextrin derived from corn, for example, has a higher GI than maltodextrin derived from rice. Additionally, the degree of polymerization, or the length of the maltodextrin chains, can also affect its GI.
Despite its high GI, maltodextrin is commonly used in sports drinks and energy bars as a quick source of energy for athletes. It is also used as a thickener or filler in processed foods. However, individuals who are looking to manage their blood sugar levels should be cautious when consuming products that contain maltodextrin and consider alternative sweeteners with lower GI values.
The Effect of Maltodextrin on Gut Health
Maltodextrin has been shown to affect gut health by altering gut bacteria composition and promoting inflammation. This can lead to various digestive issues, including bloating, gas, abdominal discomfort, and irregular bowel movements. However, the research on maltodextrin and gut health is still inconclusive, and more studies are needed to establish a causal relationship.
It is important to note that maltodextrin is commonly used as a food additive in many processed foods, such as snacks, desserts, and beverages. Therefore, it is important to read food labels carefully and limit consumption of foods that contain maltodextrin, especially for individuals with pre-existing digestive issues or conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
How to Identify Maltodextrin in Food Labels
Maltodextrin is often listed as an ingredient in food labels under the category of "carbohydrates" or "sugars." It may also be listed under its E number, E1400-E1450, depending on the country. Consumers should read food labels carefully and be aware of the amount of maltodextrin and other additives in their food products.
Alternatives to Maltodextrin: Natural Sweeteners and Substitutes
Consumers looking to reduce their maltodextrin intake can opt for natural sweeteners and substitutes, such as honey, maple syrup, stevia, or monk fruit. These sweeteners have lower glycemic indices and fewer calories than maltodextrin and are better alternatives for people with diabetes or those looking to reduce their sugar intake.
Maltodextrin in Sports Nutrition: Pros and Cons
Maltodextrin is a common ingredient in sports nutrition supplements due to its easy digestibility and quick energy release. It is often added to pre-workout supplements, energy bars, and protein powders to enhance their efficacy and aid in muscle recovery. However, excessive maltodextrin consumption can interfere with weight loss goals and may cause unwanted side effects, such as bloating, gas, and gastrointestinal distress. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts should consult their dietitians or healthcare providers before using maltodextrin-containing supplements.
The FDA Regulations on Maltodextrin in Food Products
Maltodextrin is classified as a GRAS (generally recognized as safe) substance by the FDA, meaning it is safe for consumption in moderate amounts. The FDA regulates the use of maltodextrin in food products and sets limits on its daily intake, which vary depending on age, sex, and overall health status. Consumers should follow these guidelines and consume maltodextrin in moderation.
Research Studies on the Health Effects of Maltodextrin
The scientific research on maltodextrin and its health effects is ongoing and controversial. Some studies suggest that maltodextrin may promote inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disorders, while others argue that it has no significant health risks when consumed in moderation. Consumers should be aware of the potential risks associated with maltodextrin consumption and consult their healthcare providers if they have any concerns.
Allergies and Intolerances to Maltodextrin: Symptoms and Precautions
Maltodextrin is generally safe for consumption, but some people may have allergies or intolerances to corn or other sources of starch used in its production. Symptoms of maltodextrin allergies or intolerances include rashes, hives, itching, swelling, and gastrointestinal distress. Consumers with these symptoms should avoid maltodextrin-containing products and consult their healthcare providers for alternative treatment options.
Conclusion: Is Maltodextrin Safe for Consumption?
The safety of maltodextrin largely depends on the amount and frequency of consumption, as well as individual health status, age, and other factors. While maltodextrin is generally recognized as safe by the FDA and other food safety organizations, some studies suggest that it may have potential health risks when consumed in excess. Consumers should read food labels carefully, consume maltodextrin in moderation, and consult their healthcare providers if they have any concerns.