Semaglutide, a medication commonly prescribed for type 2 diabetes and obesity, has been associated with various gastrointestinal side effects, including constipation. Understanding the relationship between Semaglutide and digestive health is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This article explores the causes behind constipation when taking Semaglutide and offers practical advice on managing and preventing this uncomfortable condition.
Key Takeaways
- Semaglutide can impact digestive health by slowing gastric emptying, which may lead to constipation.
- Individual risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and dosage can influence the likelihood of experiencing constipation on Semaglutide.
- Incorporating dietary fiber, staying hydrated, and maintaining physical activity are effective remedies for managing constipation.
- Severe cases of constipation may require medical intervention, including prescription medications or alternative therapies.
- Preventive strategies, including lifestyle modifications and regular medical follow-up, are essential to mitigate the risk of constipation on Semaglutide.
Understanding Semaglutide and Its Impact on Digestive Health
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a medication approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, more recently, for chronic weight management in adults. It belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which work by mimicking the action of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1 to regulate blood sugar levels and appetite.
Semaglutide is administered via injection, typically once a week, and is known for its ability to improve glycemic control and promote weight loss. However, its effects on the gastrointestinal system can lead to side effects, including constipation.
While Semaglutide has been a breakthrough in diabetes and obesity treatment, its impact on digestive health is a significant concern for many patients.
Understanding the balance between the benefits and potential side effects of Semaglutide is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. Effective management of side effects, such as constipation, is essential for maintaining quality of life and ensuring the continued success of the treatment.
How Semaglutide Affects the Gastrointestinal System
Semaglutide, a medication primarily used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, has been observed to influence gastrointestinal motility. The slowing down of gastric emptying is a notable effect, which can lead to symptoms such as constipation. This delay in digestion allows for extended glucose absorption, aligning with the drug's purpose of controlling blood sugar levels.
While semaglutide serves its role in managing diabetes, it is important to consider its impact on the digestive system as a whole. Patients may need to adjust their intake of certain supplements, such as a multivitamin, to ensure proper nutrient absorption.
The interaction of semaglutide with digestive enzymes and gut hormones also plays a part in its gastrointestinal effects. Here is a list of related points:
- Altered gut hormone levels affecting bowel movements
- Changes in the secretion of digestive enzymes
- Potential interaction with other medications affecting digestion
Understanding these effects is crucial for managing the side effects and maintaining overall digestive health while on semaglutide therapy.
The Link Between Semaglutide and Constipation
Semaglutide, a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity, has been associated with gastrointestinal side effects, including constipation. The slowing down of gastric emptying is a key factor contributing to this condition.
Constipation may not affect everyone using Semaglutide, but it is a recognized side effect. The medication's impact on gut motility can lead to a reduced frequency of bowel movements and harder stools. This can be particularly challenging for patients who may already have pre-existing digestive issues.
While constipation can be an uncomfortable side effect, there are several strategies that can help manage and alleviate its symptoms.
Understanding individual risk factors and how lifestyle choices interact with Semaglutide's effects is crucial for managing constipation. Here is a list of common factors that can exacerbate constipation in patients taking Semaglutide:
- Inadequate dietary fiber intake
- Low fluid consumption
- Reduced physical activity
- Pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions
- Concurrent use of other medications that slow gastrointestinal motility
Identifying the Causes of Constipation on Semaglutide
Mechanism of Action Leading to Constipation
Semaglutide, a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity, can influence gastrointestinal motility and secretion. The drug's mechanism of action may slow down intestinal transit time, leading to constipation in some patients. This effect is due to semaglutide's ability to mimic GLP-1, a hormone that regulates appetite and insulin secretion, but also impacts gut movement.
- Semaglutide's impact on the gut can also alter the balance of digestive enzymes and the processing of certain foods, such as those high in FODMAPs.
- The interaction between semaglutide and FODMAP digestive enzymes can exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms, including constipation.
While the exact interaction is complex, understanding the role of FODMAPs and digestive enzymes in constipation can help in managing the condition effectively.
Risk Factors for Developing Constipation on Semaglutide
Understanding the risk factors for constipation when using Semaglutide is crucial for prevention and management. Individuals with a predisposition to gastrointestinal issues may experience exacerbated symptoms when on this medication.
Certain dietary choices can also contribute to constipation. A diet lacking in fiber, hydration, and physical activity can increase the risk. It's important to consider the role of a low FODMAP probiotic and prebiotic regimen, as these can influence gut health and bowel regularity.
While not all patients will experience constipation, those with underlying health conditions or on concurrent medications that affect digestive motility should be particularly vigilant.
Lifestyle factors such as inadequate exercise and poor hydration can compound the constipating effects of Semaglutide. Here are some key lifestyle considerations:
- Adequate hydration
- Regular physical activity
- Balanced intake of fiber
- Incorporation of low FODMAP probiotic and prebiotic foods
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle play a pivotal role in managing constipation, especially for individuals on Semaglutide. A balanced diet rich in fiber is crucial for promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can significantly improve digestive health.
Adequate hydration is equally important. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps soften stool and stimulates bowel movements.
Physical activity is another key component. Regular exercise, even mild activities like walking, can help stimulate intestinal contractions and alleviate constipation.
Here are some lifestyle tips to consider:
- Increase fiber intake gradually to avoid gas and bloating.
- Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Include physical activity in your daily routine, aiming for 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Be mindful of the timing of meals and try to establish a regular eating schedule.
Practical Remedies for Managing Constipation Induced by Semaglutide
Dietary Adjustments and Fiber Intake
Making dietary adjustments is a key step in managing constipation caused by Semaglutide. Increasing fiber intake can significantly improve bowel movements. However, it's important to do this gradually to prevent gas and bloating. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Start by incorporating a variety of high-fiber foods into your meals.
- Aim for a balanced diet that includes a mix of soluble and insoluble fiber.
- Consider a fiber supplement if dietary changes aren't sufficient.
Ensuring adequate fiber intake not only helps with constipation but also supports overall digestive health. Remember to increase fiber in your diet slowly to allow your digestive system to adjust.
Hydration is equally important when increasing fiber; aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day. Regular physical activity can also help stimulate intestinal function and relieve constipation.
Hydration and Physical Activity
Ensuring adequate hydration is crucial when managing constipation induced by Semaglutide. Drinking sufficient water can help soften stools and stimulate bowel movements. It's recommended to consume at least 8 glasses of water daily, but this may vary based on individual needs and activity levels.
Physical activity is another key component in alleviating constipation. Regular exercise, even mild forms like walking, can greatly enhance gut motility. Incorporating physical activity into daily routines can be planned alongside meal plans to ensure a holistic approach to digestive health.
While hydration and exercise are important, they should be complemented with other constipation remedies for optimal results.
Here are some simple tips to integrate hydration and physical activity into your daily life:
- Start your day with a glass of water to activate your digestive system.
- Carry a water bottle and sip throughout the day.
- Include water-rich foods in your meal plans, such as fruits and vegetables.
- Schedule short walks or stretching breaks, especially after meals.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to suit your fitness level.
Over-the-Counter Solutions and When to Use Them
For individuals experiencing constipation while on Semaglutide, over-the-counter (OTC) options can be a practical choice. Psyllium, a type of soluble fiber, is a common OTC remedy that can help to alleviate symptoms of constipation. It works by absorbing water in the gut, making stools softer and easier to pass.
When considering OTC solutions, it's important to understand when they are appropriate to use:
- Mild to moderate constipation: OTC fiber supplements like psyllium can be effective.
- Persistent symptoms: If constipation continues despite dietary changes and increased fiber intake, OTC laxatives may be necessary.
- Before using stimulant laxatives: These should be a last resort as they can cause dependency.
Always start with the lowest effective dose of any OTC remedy and increase gradually as needed. It's crucial to read labels and follow dosing instructions to avoid potential side effects.
If constipation persists or is accompanied by severe pain, it may indicate a more serious condition, and medical advice should be sought. Remember, while OTC solutions can provide relief, they are not a substitute for professional medical treatment.
Medical Interventions for Severe Cases of Constipation
When to Seek Medical Attention
Constipation can often be managed with simple home remedies; however, there are times when medical attention is necessary. If you experience severe pain, blood in your stools, or constipation lasting more than two weeks while on Semaglutide, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional. These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition.
While incorporating a low FODMAP probiotic into your routine can be beneficial for gut health, it's important to recognize when symptoms are beyond self-care. Persistent or worsening constipation requires professional evaluation.
In addition to these warning signs, be aware of any new or unusual symptoms that may arise. Here's a quick checklist to help you decide when to seek medical help:
- Sudden changes in bowel habits
- Intense abdominal pain
- Signs of dehydration
- Unintended weight loss
- Inability to pass gas
Remember, timely intervention can prevent complications and ensure that you receive the appropriate treatment for your condition.
Prescription Medications and Their Use
In cases where over-the-counter solutions are insufficient, prescription medications may be necessary to alleviate constipation caused by Semaglutide. One such medication that may be prescribed is glutamine, which can help improve intestinal function.
- Laxatives: Stimulate bowel movements or soften stool.
- Stool softeners: Make stool easier to pass.
- Prokinetic agents: Enhance gastrointestinal motility.
While these medications can be effective, they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Alternative Therapies and Procedures
For individuals with severe constipation induced by Semaglutide, where standard medical interventions are insufficient, alternative therapies and procedures may be considered. Biofeedback therapy, for instance, has shown promise in managing constipation by helping patients improve bowel movement coordination.
In addition to biofeedback, acupuncture and certain herbal remedies have been explored as potential treatments. While evidence for their effectiveness is still emerging, some patients report relief from constipation symptoms.
Other procedures, such as sacral nerve stimulation or surgery, are reserved for the most refractory cases. These interventions are typically considered when all other options have failed and the patient's quality of life is significantly impacted. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before pursuing any alternative therapies or procedures.
Preventive Strategies to Avoid Constipation on Semaglutide
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Management
Adopting certain lifestyle modifications can be instrumental in managing constipation for those on Semaglutide. Regular physical activity is crucial as it stimulates bowel movements and enhances digestive health. Incorporating a variety of exercises, from brisk walking to yoga, can make a significant difference.
Diet also plays a vital role in preventing constipation. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains ensures adequate fiber intake, which is essential for bowel regularity. It's important to be mindful of one's eating habits and make adjustments as needed.
Stress management should not be overlooked, as stress can negatively impact gastrointestinal function. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and adequate sleep can help mitigate stress levels.
While these lifestyle changes are beneficial, it's also helpful to explore additional resources for digestive health. A website page offers resources, blogs, podcasts, and products related to digestive health, including FODMAP diet tools, low FODMAP meal plans, and Amazon affiliate products.
Monitoring and Adjusting Semaglutide Dosage
Monitoring and adjusting the dosage of Semaglutide is crucial for both efficacy and minimizing side effects, including constipation. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to find the optimal dose that manages their condition while reducing the risk of gastrointestinal discomfort.
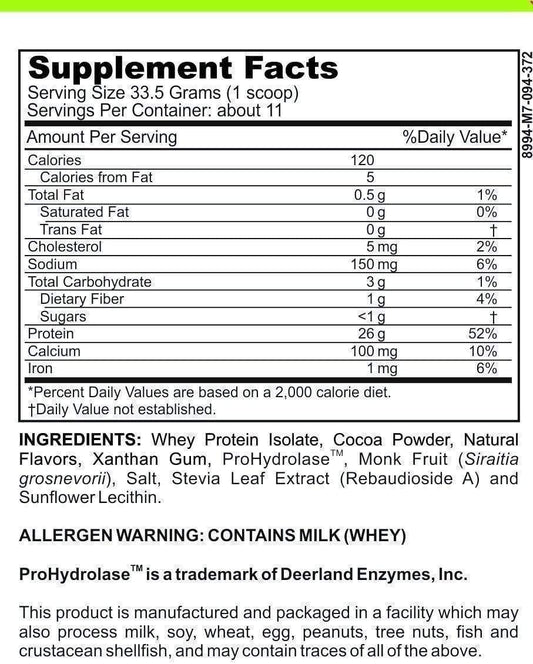
Regular dosage assessments can help in identifying the need for adjustments. For instance, if a patient experiences constipation, a healthcare provider might suggest a temporary reduction in dosage. Additionally, incorporating a low FODMAP chocolate whey protein powder into the diet may assist in managing symptoms while ensuring adequate protein intake.
It's important to note that any dietary supplement, including protein powders, should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure they are compatible with Semaglutide therapy and do not exacerbate constipation.
Patients should maintain a symptom diary to track their response to Semaglutide and any dietary changes. This record can be invaluable during medical appointments to make informed decisions about dosage adjustments.
The Importance of Regular Medical Follow-Up
Regular medical follow-up is crucial for individuals on Semaglutide to ensure optimal management of constipation and overall treatment efficacy. Regular consultations allow healthcare providers to monitor the patient's response to the medication and adjust dosages as necessary.
- During these visits, patients can discuss any new or worsening symptoms, including constipation.
- Healthcare professionals may recommend incorporating natural supplements like ashwagandha, which some studies suggest could support digestive health.
- It's also an opportunity to review and reinforce dietary and lifestyle changes that can alleviate constipation.
Ensuring a consistent follow-up schedule can prevent the escalation of constipation and other side effects, leading to a better quality of life for patients on Semaglutide.
Managing your digestive health while on Semaglutide is crucial, and incorporating the right preventive strategies can make all the difference. To avoid constipation and maintain a healthy gut, explore our range of gut-friendly supplements and personalized meal plans. Our products are scientifically formulated to support your digestive system. Don't let constipation hold you back—visit our website today for expert advice and tailored solutions that cater to your unique needs. Take the first step towards a comfortable and healthy life.
Conclusion
In summary, constipation is a potential side effect of semaglutide, a medication commonly used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Understanding the causes of this gastrointestinal issue can help patients and healthcare providers take proactive steps to mitigate its impact. Adequate hydration, dietary adjustments, and regular physical activity are key strategies in managing constipation. Additionally, over-the-counter remedies and medical consultations can provide relief when necessary. It's important for patients to communicate with their healthcare team about any side effects they experience on semaglutide to ensure a comprehensive approach to their treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Semaglutide and how does it affect the body?
Semaglutide is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by mimicking a hormone that regulates appetite and insulin secretion, which can impact digestive health and potentially lead to constipation.
Why does Semaglutide cause constipation?
Semaglutide can slow down gastric emptying, meaning food passes through the digestive system more slowly. This can lead to decreased bowel movements and result in constipation.
Are there specific risk factors for developing constipation on Semaglutide?
Risk factors may include a low-fiber diet, inadequate hydration, sedentary lifestyle, and individual sensitivity to the medication's gastrointestinal effects.
What dietary adjustments can help manage constipation caused by Semaglutide?
Increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as ensuring adequate fluid consumption, can help alleviate constipation.
When should I seek medical attention for constipation while taking Semaglutide?
If you experience severe discomfort, blood in your stools, or constipation that doesn't improve with home remedies, it's important to seek medical attention.
Can adjusting the dosage of Semaglutide reduce constipation symptoms?
In some cases, adjusting the dosage under medical supervision can help manage side effects such as constipation. However, this should only be done in consultation with a healthcare provider.