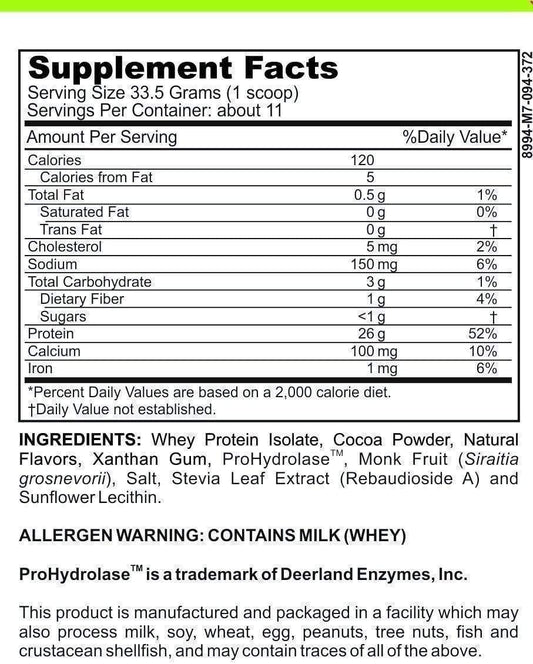
What Are Low FODMAP Foods For Reflux
Reflux is a common gastrointestinal condition that occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, causing a range of uncomfortable symptoms. While there are various factors that contribute to reflux, diet is often a key player in managing and preventing episodes. One dietary approach that has gained attention in recent years is the low FODMAP diet. In this article, we will explore the role of low FODMAP foods in managing reflux and why they may be beneficial in reducing symptoms.
Understanding Reflux and Its Causes
Reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when the muscular ring at the bottom of the esophagus (lower esophageal sphincter) fails to close properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back up into the esophagus. This can lead to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and a sour taste in the mouth.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of reflux. These include obesity, hiatal hernia, certain medications, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. In addition to these factors, diet plays a significant role in managing reflux.
When it comes to managing reflux, understanding the role of diet is crucial. Dietary choices can greatly impact the severity and frequency of reflux symptoms. Certain foods and beverages have been identified as common triggers for reflux, including spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, caffeine, fatty foods, and carbonated beverages. These foods can irritate the esophagus and increase the production of stomach acid, making reflux symptoms worse.
On the other hand, there are also foods that can help alleviate reflux symptoms. These include non-citrus fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. These foods are generally easier to digest and less likely to trigger reflux.
The Role of Diet in Managing Reflux
Dietary choices play a significant role in managing reflux. By making smart food choices, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of reflux symptoms. In addition to avoiding trigger foods, it is also important to eat smaller, more frequent meals and to avoid lying down immediately after eating. These simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference in managing reflux.
Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing reflux. Obesity can increase the pressure on the stomach, causing the lower esophageal sphincter to weaken and allowing stomach acid to flow back up into the esophagus. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of reflux.
What is a Low FODMAP Diet?
A low FODMAP diet is a specialized eating plan designed to manage digestive symptoms in individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). FODMAPs are a group of fermentable carbohydrates that can be poorly absorbed in the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain.
The acronym FODMAP stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols. These are short-chain carbohydrates found in a variety of foods, including certain fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy products, and sweeteners. While these foods are generally healthy, they can cause discomfort and digestive issues in individuals with IBS.
By reducing or eliminating high FODMAP foods from the diet, individuals with IBS can often experience relief from their symptoms. This involves working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to identify trigger foods and create a personalized low FODMAP meal plan. The low FODMAP diet is not a long-term solution, but rather a short-term elimination diet followed by a reintroduction phase to identify specific trigger foods.
In conclusion, understanding reflux and its causes is essential for managing this condition. By making dietary changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and following a low FODMAP diet if necessary, individuals can effectively manage their reflux symptoms and improve their quality of life.
The Connection Between FODMAPs and Reflux
While the low FODMAP diet was originally developed for managing IBS symptoms, there is growing evidence to suggest that it may also benefit individuals with reflux. This is because certain high FODMAP foods can contribute to reflux symptoms by increasing stomach acid production, slowing down digestion, and causing excessive gas production, which can put pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter.
How FODMAPs Affect Digestion
When high FODMAP foods are consumed, they can attract water into the intestinal tract and be fermented by bacteria in the large intestine. This can lead to increased gas production and bloating, which can contribute to reflux symptoms. Additionally, the fermentation process can produce byproducts that may irritate the lining of the esophagus and trigger reflux episodes.
For example, foods high in fructose, such as apples and pears, can be difficult to digest for individuals with reflux. Fructose is a type of FODMAP that can cause fermentation in the gut, leading to the production of gas and potentially triggering reflux symptoms. By avoiding high fructose foods, individuals with reflux can reduce the risk of experiencing uncomfortable symptoms.
In addition to fructose, other FODMAPs like lactose and polyols can also affect digestion and contribute to reflux. Lactose, found in dairy products, can be challenging for some individuals to break down, leading to increased gas production and potential reflux symptoms. Polyols, which are sugar alcohols found in certain fruits and artificial sweeteners, can also be poorly absorbed by the body and cause digestive discomfort.
Why Low FODMAP Foods May Help with Reflux
By following a low FODMAP diet, individuals with reflux may be able to reduce their intake of these potentially problematic carbohydrates and alleviate symptoms. Low FODMAP foods are typically easier to digest, require less stomach acid for breakdown, and produce less gas during the fermentation process.
For example, opting for low FODMAP fruits like bananas and grapes can provide essential nutrients without triggering reflux symptoms. These fruits are lower in fructose and polyols compared to high FODMAP fruits like apples and cherries. Similarly, choosing lactose-free dairy alternatives or lactose-reduced products can help individuals with reflux enjoy dairy without the discomfort.
It is important to note that while a low FODMAP diet may provide relief for some individuals with reflux, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Reflux can have various underlying causes, and it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
Identifying Low FODMAP Foods
When following a low FODMAP diet, it is essential to understand which foods are considered low in FODMAPs and which should be limited or avoided. While the diet can be complex, there are many resources available that provide lists of low FODMAP foods, making it easier to plan meals and snacks.
One of the key aspects of a low FODMAP diet is being able to identify and incorporate low FODMAP foods into your daily meals. By doing so, you can help alleviate symptoms associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other digestive disorders. It's important to note that FODMAPs are a group of carbohydrates that can be poorly absorbed in the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain.
Common Low FODMAP Foods
Some examples of low FODMAP foods include certain fruits like bananas, blueberries, and oranges; vegetables such as carrots, cucumbers, and spinach; proteins like chicken, turkey, and tofu; grains like rice, oats, and gluten-free products; and dairy alternatives such as lactose-free milk and hard cheeses.
Let's take a closer look at these low FODMAP foods:
1. Fruits: Bananas are not only delicious but also low in FODMAPs, making them a great choice for those following a low FODMAP diet. Blueberries and oranges are also low in FODMAPs and can be enjoyed in moderation. These fruits provide essential vitamins and minerals, while being gentle on the digestive system.
2. Vegetables: Carrots, cucumbers, and spinach are all excellent choices for those on a low FODMAP diet. Carrots are not only crunchy and flavorful but also packed with nutrients. Cucumbers are refreshing and hydrating, while spinach is a versatile leafy green that can be added to salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes.
3. Proteins: Chicken, turkey, and tofu are all low FODMAP protein sources that can be incorporated into various meals. These options provide essential amino acids and are versatile enough to be used in a wide range of recipes.
4. Grains: Rice, oats, and gluten-free products are all low FODMAP grains that can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet. Rice is a staple food in many cuisines and can be paired with vegetables and proteins for a satisfying meal. Oats are a great source of fiber and can be enjoyed as oatmeal or added to baked goods. Gluten-free products provide alternatives for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
5. Dairy Alternatives: Lactose-free milk and hard cheeses are suitable options for individuals who are lactose intolerant or following a low FODMAP diet. These alternatives allow individuals to enjoy dairy flavors without the discomfort associated with lactose intolerance.
Foods to Avoid on a Low FODMAP Diet
While there are many foods that can be enjoyed on a low FODMAP diet, there are also several high FODMAP foods that should be limited or avoided to reduce reflux symptoms. These include foods such as onions, garlic, apples, pears, wheat-based products, certain legumes, and high lactose dairy products.
It's important to be mindful of these high FODMAP foods as they can trigger symptoms in individuals with sensitive digestive systems. Onions and garlic, for example, are known to contain high levels of FODMAPs and can cause bloating and discomfort. Apples and pears, although nutritious, can also be high in FODMAPs and may need to be avoided or consumed in small quantities.
Wheat-based products, such as bread, pasta, and pastries, can be problematic for individuals with gluten sensitivities or those following a low FODMAP diet. Legumes, including beans and lentils, can also be high in FODMAPs and may cause digestive distress in some individuals. Lastly, high lactose dairy products, such as milk and soft cheeses, can be challenging for those with lactose intolerance or individuals following a low FODMAP diet.
By being aware of these high FODMAP foods, individuals can make informed choices when planning their meals and snacks. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any significant dietary changes, especially if you have specific medical conditions or dietary restrictions.
Incorporating Low FODMAP Foods into Your Diet
Adopting a low FODMAP eating plan can seem challenging at first, but with some guidance and creativity, it is possible to enjoy a balanced and flavorful diet while reducing reflux symptoms.
Tips for a Balanced Low FODMAP Diet
When following a low FODMAP diet, it is important to ensure you are still getting all the necessary nutrients. Here are some tips to help you maintain a balanced eating plan:
- Include a variety of low FODMAP fruits, vegetables, proteins, and grains in your meals.
- Experiment with herbs, spices, and low FODMAP flavor enhancers to add taste to your dishes.
- Opt for gluten-free products if you need to avoid wheat-containing foods.
- Consider working with a registered dietitian who specializes in the low FODMAP diet to ensure you are meeting your nutritional needs.
Overcoming Challenges of a Low FODMAP Diet
It is common to face challenges when embarking on a new dietary approach. Some common challenges of a low FODMAP diet include difficulty finding suitable food options when dining out, managing social situations that involve food, and feeling overwhelmed by the restrictions of the diet. Learning strategies to navigate these challenges can significantly improve adherence and overall satisfaction with the diet.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you are experiencing persistent reflux symptoms or are considering trying a low FODMAP diet, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and support.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If reflux symptoms are severe, frequent, or are interfering with your quality of life, it is recommended to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, determine the most appropriate treatment plan, and rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your reflux.
Working with a Dietitian for a Personalized Plan
A registered dietitian who specializes in gastrointestinal conditions can be a valuable resource when it comes to incorporating low FODMAP foods into your diet. They can assess your individual needs, provide guidance on meal planning, assist with food reintroduction after the elimination phase, and help you develop a sustainable eating plan that supports your reflux management goals.
In conclusion, low FODMAP foods can play a significant role in managing reflux symptoms. By understanding the connection between FODMAPs and reflux, identifying low FODMAP foods, and incorporating them into your diet, you may find relief from the discomfort of reflux. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and support on your reflux management journey.