Complementary Medicine: Inflammatory Bowel Disease Explained
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a term that describes conditions characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The two most common types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. This glossary entry will delve into the world of complementary medicine and its role in managing and treating IBD. Complementary medicine refers to treatments that are used along with standard medical treatments, but are not considered standard themselves. These can include herbs, dietary supplements, acupuncture, yoga, and more.
It's important to note that while these treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life, they should not replace conventional medical treatments. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen. This glossary entry will provide a comprehensive understanding of the different complementary medicine approaches and how they can be utilized in the management of IBD.
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a term used to describe disorders that involve chronic inflammation of your digestive tract. Types of IBD include ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Ulcerative colitis involves inflammation and sores in the innermost lining of your large intestine (colon) and rectum. Crohn's disease is characterized by inflammation of the lining of your digestive tract, which can occur in any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the anus.
IBD can be debilitating and sometimes leads to life-threatening complications. While it has no known cure, treatment can greatly reduce its signs and symptoms and even bring about long-term remission.
Causes of IBD
The exact cause of IBD remains unknown. Previously, diet and stress were suspected, but now doctors know that these factors may aggravate but don't cause IBD. One possible cause is an immune system malfunction. When your immune system tries to fight off an invading virus or bacterium, an abnormal immune response causes the immune system to attack the cells in the digestive tract, too.
Hereditary factors also seem to play a role in that IBD is more common in people who have family members with the disease. However, most people with IBD don't have this family history.
Symptoms of IBD
Symptoms related to inflammation of the bowel can include diarrhea, rectal bleeding, urgent need to move bowels, abdominal cramps and pain, sensation of incomplete evacuation, and constipation (which can lead to bowel obstruction). Other symptoms may include weight loss, fatigue, night sweats, and loss of appetite.
There are also symptoms that are not related to the digestive system, such as arthritis, skin disorders, inflammation in the eyes or mouth, kidney stones, gallstones, or other diseases of the liver and biliary system. Some of these conditions can occur before the bowel symptoms.
Complementary Medicine for IBD
Complementary medicine for IBD involves the use of non-standard therapies alongside conventional treatments. These therapies can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and promote overall wellness. They do not replace standard medical treatments, but can provide additional benefits when used appropriately.
It's important to note that not all complementary therapies are safe for everyone, and some can interact with standard medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen.
Dietary Supplements
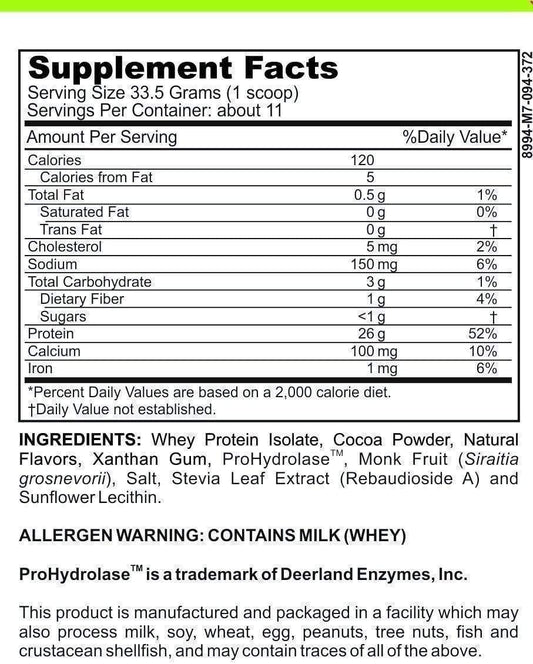
Some people with IBD find that dietary supplements can help manage their symptoms. These can include probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in your gut. Other supplements that may be beneficial include omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation, and vitamins and minerals to replace any deficiencies caused by the disease.
However, not all supplements are safe for everyone, and some can interact with standard medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine involves the use of plants or plant extracts to treat illness and promote health. Some herbs that may be beneficial for people with IBD include aloe vera, which can help soothe the digestive tract, and turmeric, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
However, not all herbs are safe for everyone, and some can interact with standard medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new herbal regimen.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of traditional Chinese medicine that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It's thought to help balance the body's energy and promote healing. Some people with IBD find that acupuncture can help manage their symptoms.
However, not all forms of acupuncture are safe for everyone, and some can interact with standard medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new acupuncture regimen.
Mind-Body Therapies
Mind-body therapies are treatments that are designed to help the mind's ability to affect bodily function and symptoms. These can include techniques like meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises. Some people with IBD find that these therapies can help manage stress and reduce their symptoms.
However, not all mind-body therapies are safe for everyone, and some can interact with standard medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new mind-body therapy regimen.
Conclusion
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive treatment approach. Complementary medicine can play an important role in managing IBD, alongside conventional medical treatments. Whether it's through dietary supplements, herbal medicine, acupuncture, or mind-body therapies, there are many ways that complementary medicine can help improve quality of life for people with IBD.
However, it's important to remember that not all complementary therapies are safe for everyone, and some can interact with standard medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen. With the right approach, it's possible to manage IBD and lead a healthy, fulfilling life.